-ˋˏ ༻ 10 ༺ ˎˊ-
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
The First Alternate Reality
𖤓
The Science Being Used
This will be a list of the scientific concepts and the purpose they are given
Characters
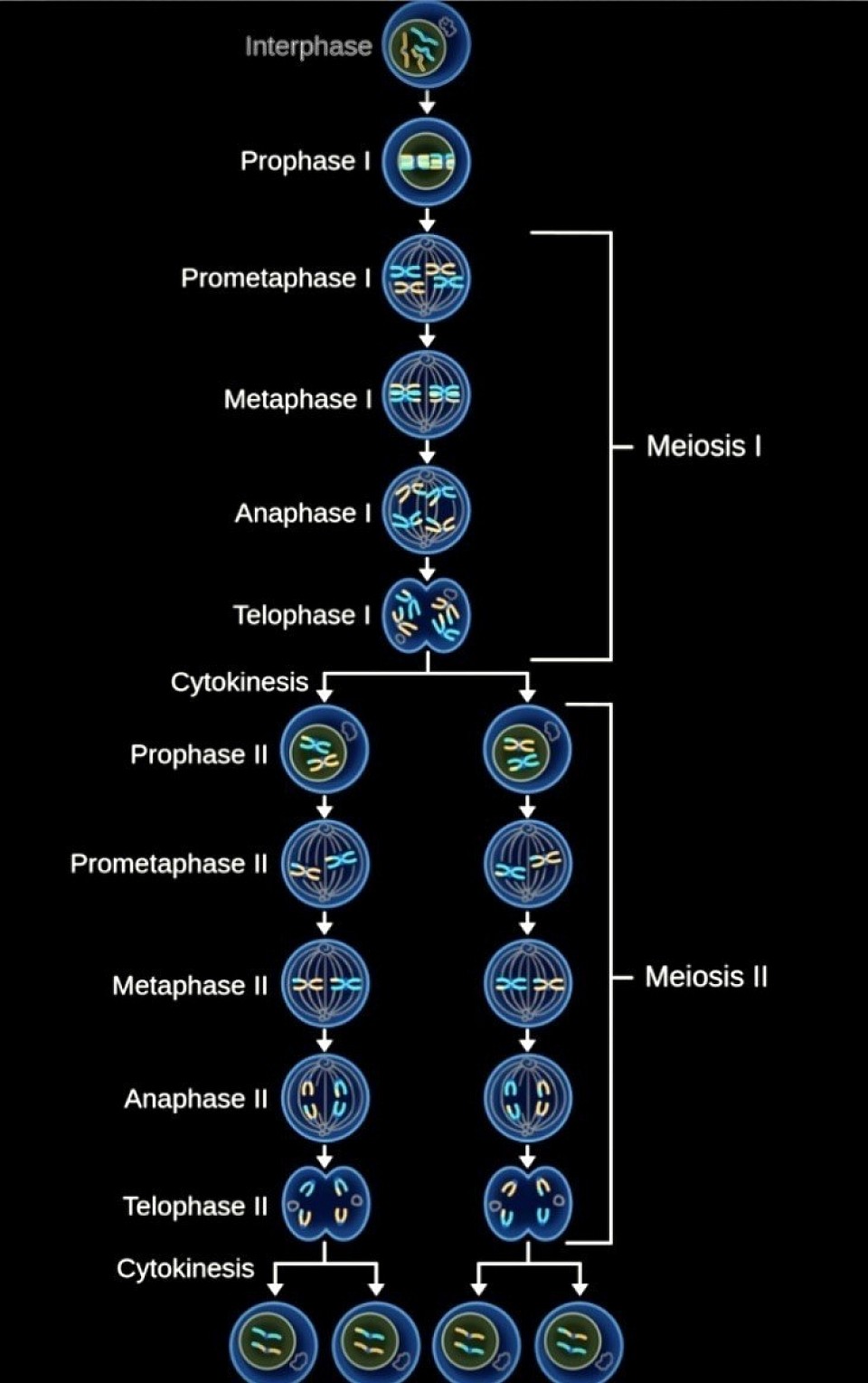
Using meiosis for characters
Laminae One
The first character type to assimilate
Laminae Two
The second to assimilate
Laminae Three
The third to assimilate
Laminae Four
The fourth to assimilate
What are the nations identities
And how do the people react
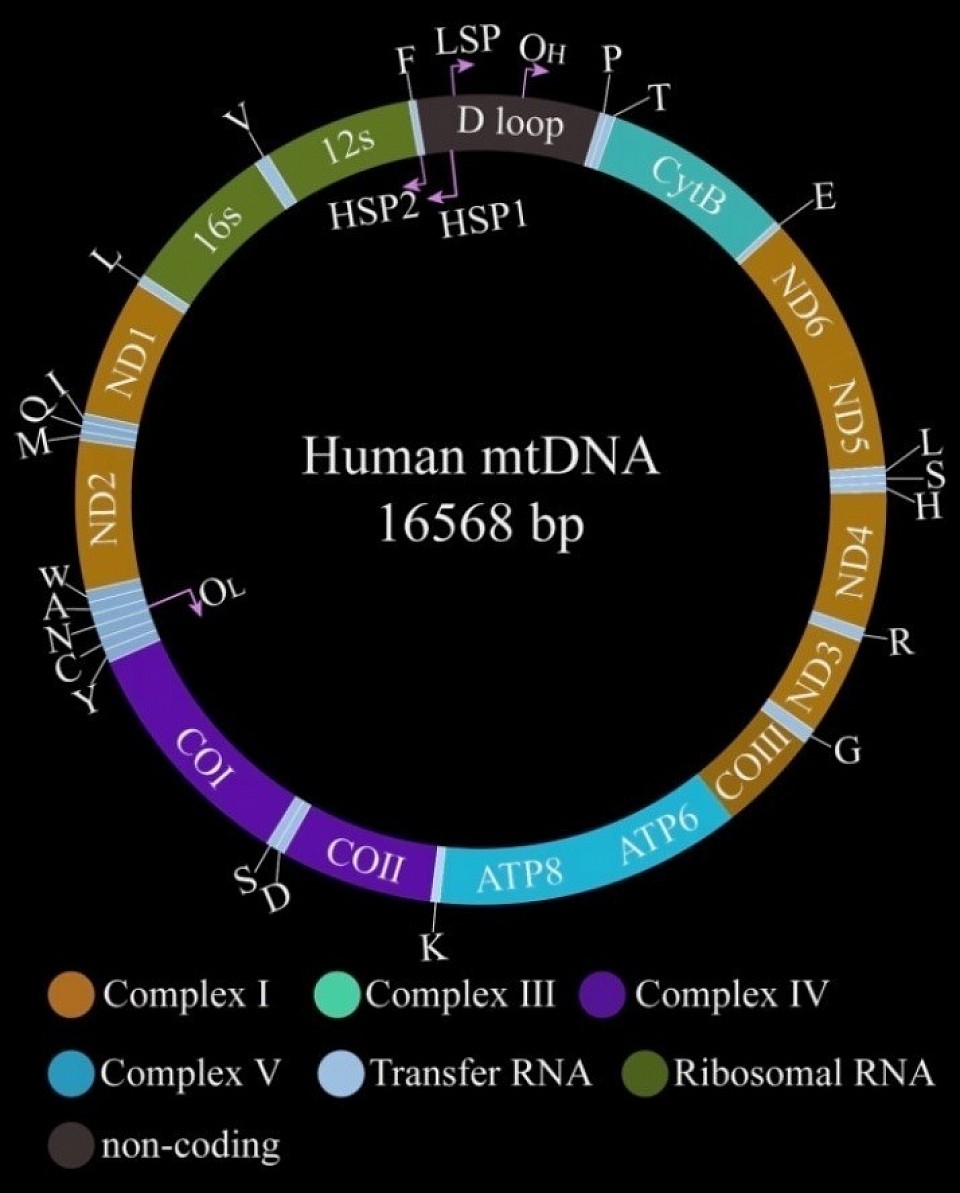
The reaction to mitochondrial DNA
The characters reaction
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
Characters
What stays with the personality of the people is the side of Laminae
The other aspect of their personality slowly changes as they assimilate into a new world
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
Page:1 - 2