-ˋˏ ༻ 7 ༺ ˎˊ-
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
The Nation of Plas
The identity of a nation, it’s history and culture
The Evolution of Plas
⋆˚𝜗𝜚˚⋆
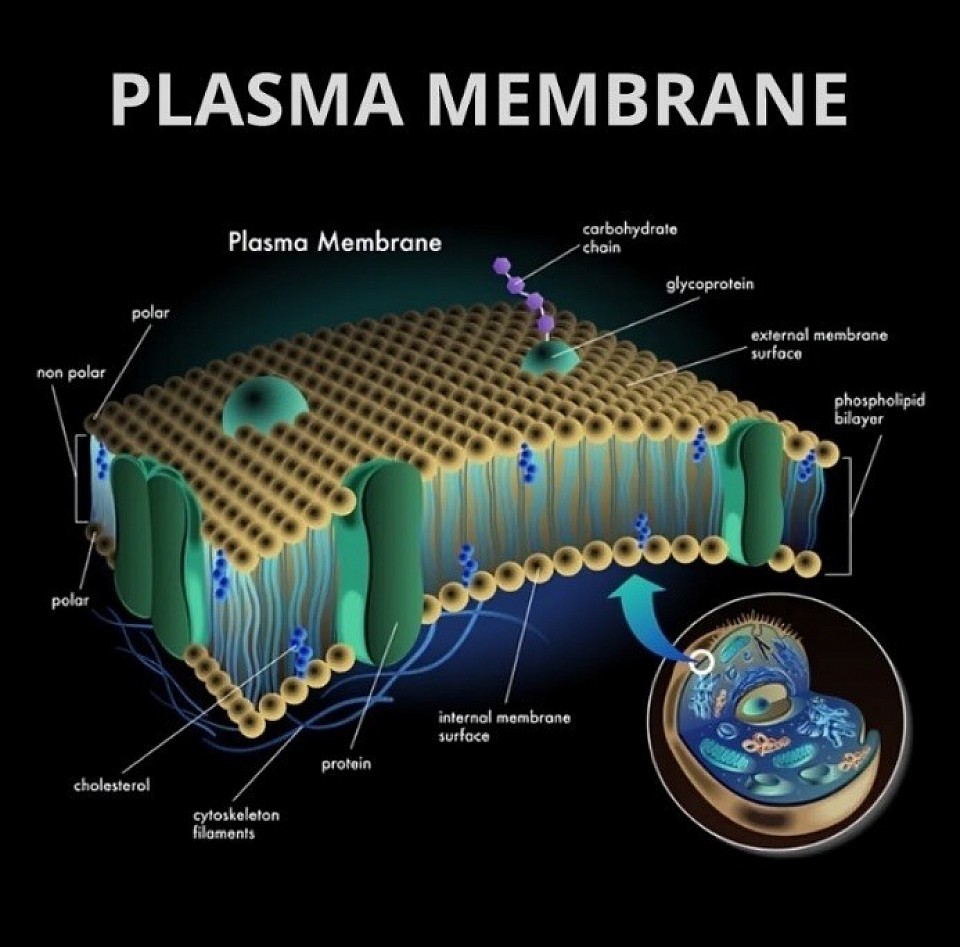
The Nature of Plas
It's made up of two layers of phospholipids
It's made up of phospholipids
It contains integral proteins that are permanently embedded in the membrane
It regulates what enters and exits the cell
It prevents harmful materials from entering the cell
It helps cells communicate
It helps cells carry out changes triggered by chemical messengers
It helps cells transport and share material
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain materials to pass through and blocking others
𖤓
Plas’ Identity
How do the people react
Questions
Questions that shape the culture
The Corruption of Plas
The activities and events of a falling society
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
Opinions on the Dead
Opinions on the world of the dead
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
Type One Personality
How do they react
Before Transcendence
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
After Corruption
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
During Transcendence
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
After Transcendence
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
⟁
Type Two Personality
How do they react
Before Transcendence
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
After Corruption
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
During Transcendence
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────